2 快速移植一个UAC+HID复合设备
按照前面两篇文章,我们可以快速的移植出一个基于TinyUSB的UAC+HID复合设备,主要的代码片段如下:
/*------------- MAIN -------------*/
int main(void)
{
USB_DeviceClockInit();//board_init();
CONSOLE_Init(460800); //enable printf debug
// init device stack on configured roothub port
tud_init(BOARD_TUD_RHPORT);
TU_LOG1("UAC Headset & HID runningrn"); // CFG_TUSB_DEBUG for debugging #if CFG_TUSB_DEBUG
// 0 : no debug
// 1 : print error
// 2 : print warning
// 3 : print info
while (1)
{
tud_task(); // TinyUSB device task
audio_task();
hid_task();
}
return 0;
}
#define EPNUM_AUDIO_IN 0x01
#define EPNUM_AUDIO_OUT 0x01
#define EPNUM_HID 0x03
uint8_t const desc_configuration[] =
{
// Interface count
string index
total length, attribute, power in mA
TUD_CONFIG_DESCRIPTOR(1
ITF_NUM_TOTAL, 0
CONFIG_TOTAL_LEN, TUSB_DESC_CONFIG_ATT_REMOTE_WAKEUP, 100),
// Interface number
string index
EP Out & EP In address, EP size
TUD_AUDIO_HEADSET_STEREO_DESCRIPTOR(2
EPNUM_AUDIO_OUT, EPNUM_AUDIO_IN | 0x80),
// Interface number
string index
protocol, report descriptor len, EP Out & In address, size & polling interval
TUD_HID_INOUT_DESCRIPTOR(ITF_NUM_HID, 6
HID_ITF_PROTOCOL_NONE, sizeof(desc_hid_report), EPNUM_HID, 0x80 | EPNUM_HID, CFG_TUD_HID_EP_BUFSIZE, 10),
};
//------------------------------+
// String Descriptors
//------------------------------+
// array of pointer to string descriptors
char const* string_desc_arr [] =
{
(const char[]) { 0x09, 0x04 }, // 0: is supported language is English (0x0409)
"TinyUSB"
// 1: Manufacturer
"TinyUSB headset"
// 2: Product
"000001"
// 3: Serials, should use chip ID
"TinyUSB Speakers"
// 4: Audio Interface
"TinyUSB Microphone"
// 5: Audio Interface
"TinyUSB HID"
// 6: HID Interface
};
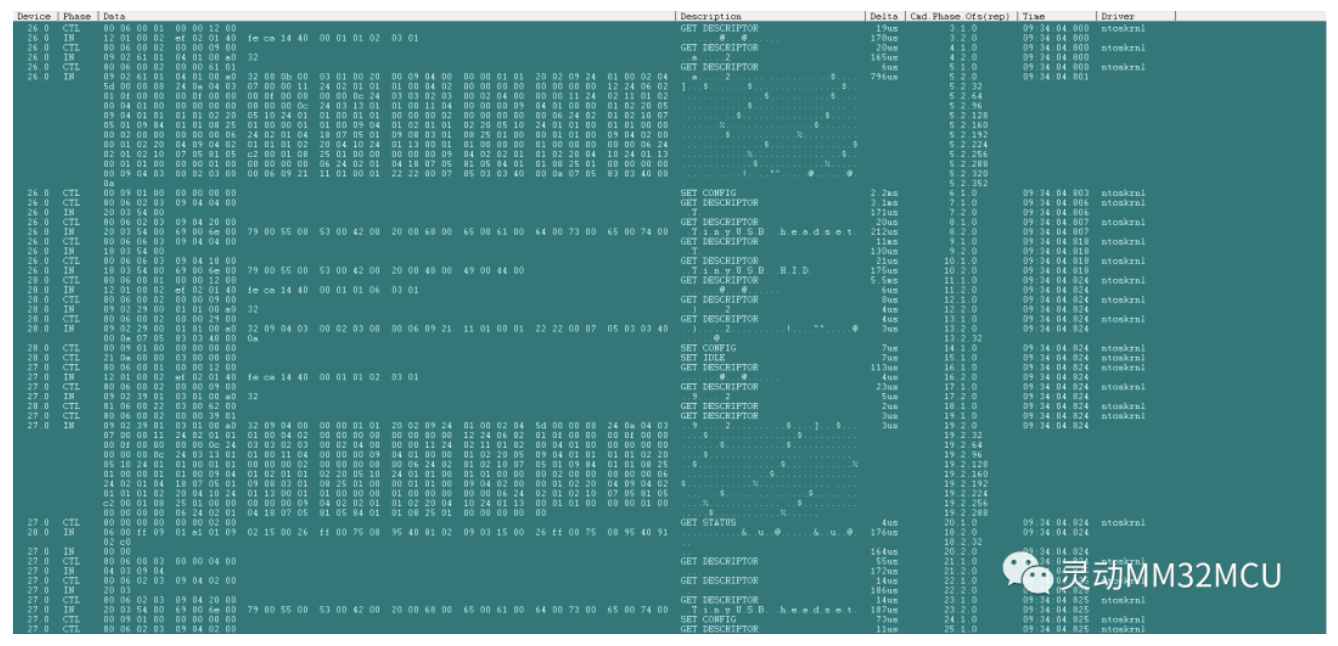
图1 枚举过程
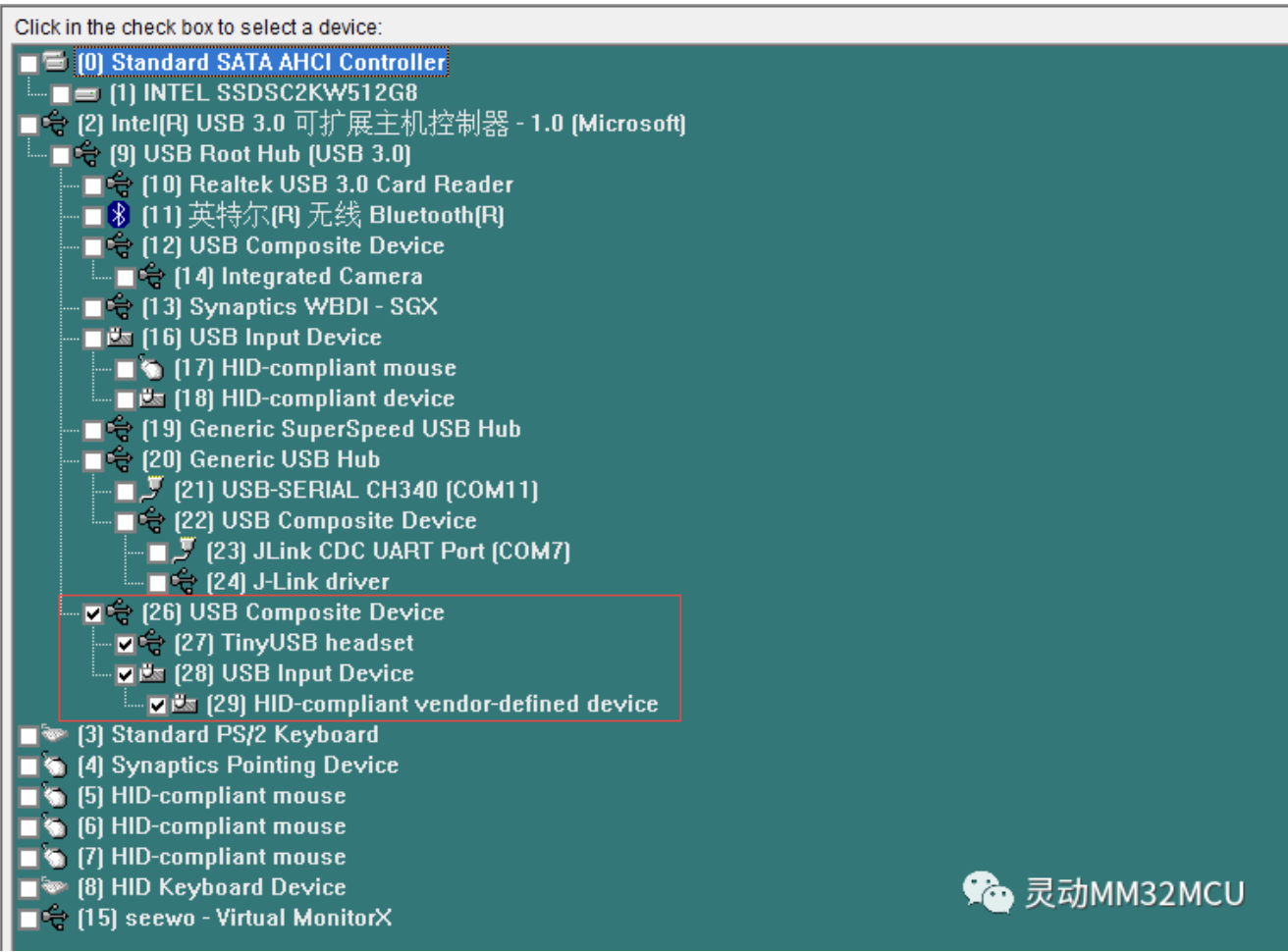
图2 枚举设备
工程文件树:

3 耳机设备设置修改音量
在耳机属性里面可以操作修改音量大小,同时通过抓包工具可以抓到主机下发的SET CUR命令。
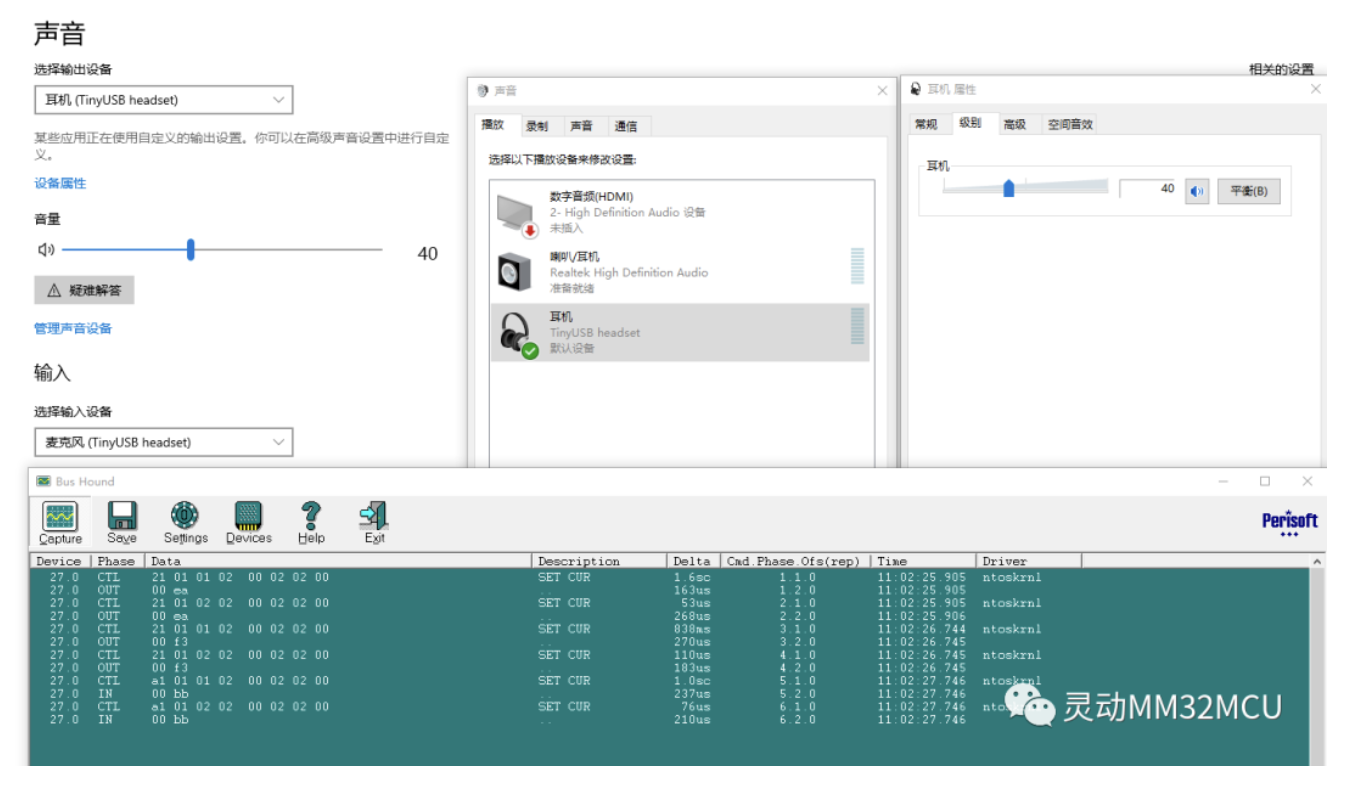
图3 设置音量
4 耳机设备设置修改采样频率和位深度
在耳机属性高级里面默认格式可以看到下拉框有两种格式,一个是2通道 16位48000Hz,另外一个是2通道 24位 48000Hz,播放声音下发ISOC包的时候根据这个选择传输。
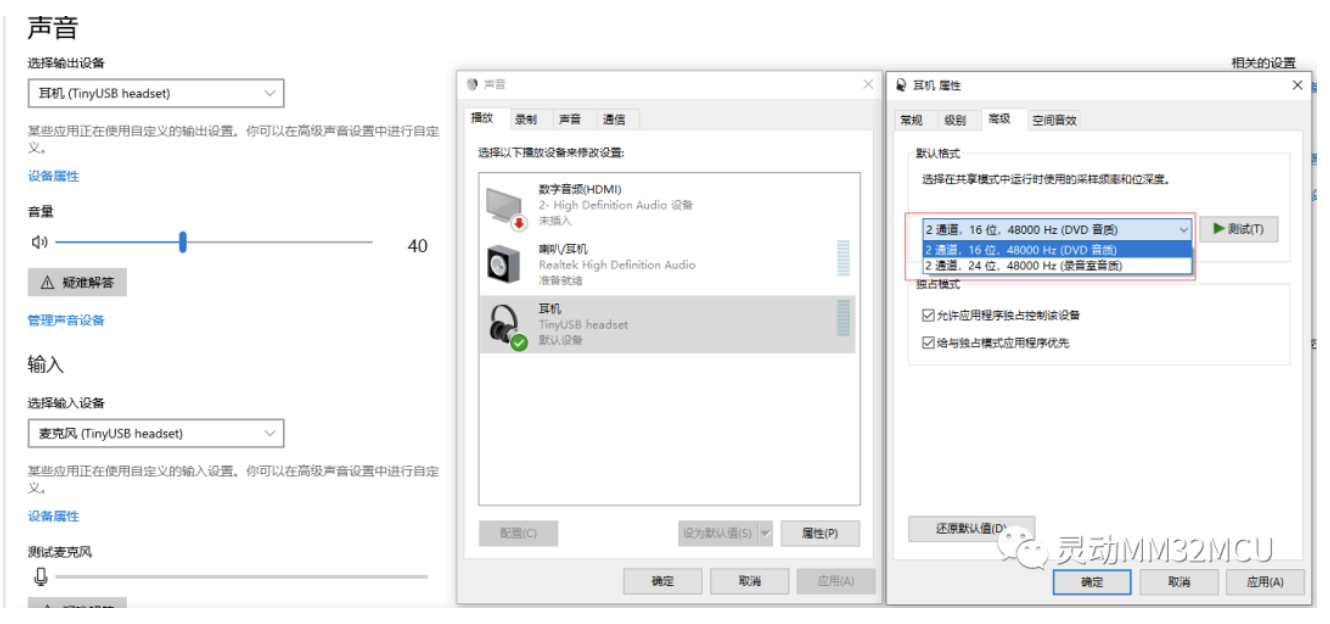
图4 设置采样频率和位深度
通过设置,下位机可以在播放或者录音时处理不同的采样频率和位深度。样例中全局变量current_resolution是位深度,current_sample_rate是采样频率。
5 音频数据的收发处理
播放时ISOC下发的数据包缓存在spk_buf里面。
录用时麦克风的声音采样数据写入mic_buf,通过ISOC同步上传到电脑端。(例程是将播放的数据包处理后通过接口又返回电脑端,由tud_audio_write((uint8_t * ) mic_buf, (uint16_t) (spk_data_size / 2))实现)
//------------------------------+
// AUDIO Task
//------------------------------+
void audio_task(void)
{
// When new data arrived, copy data from speaker buffer, to microphone buffer
// and send it over
// Only support speaker & headphone both have the same resolution
// If one is 16bit another is 24bit be care of LOUD noise !
if (spk_data_size)
{
if (current_resolution == 16)
{
int16_t *src = (int16_t*)spk_buf;
int16_t *limit = (int16_t*)spk_buf + spk_data_size / 2;
int16_t *dst = (int16_t*)mic_buf;
while (src < limit)
{
// Combine two channels into one
int32_t left = *src++;
int32_t right = *src++;
*dst++ = (int16_t) ((left > > 1) + (right > > 1));
}
memset(mic_buf,0xCC
sizeof(mic_buf)); //mm32 test code
tud_audio_write((uint8_t *)mic_buf, (uint16_t) (spk_data_size / 2));
spk_data_size = 0;
}
else if (current_resolution == 24)
{
int32_t *src = spk_buf;
int32_t *limit = spk_buf + spk_data_size / 4;
int32_t *dst = mic_buf;
while (src < limit)
{
// Combine two channels into one
int32_t left = *src++;
int32_t right = *src++;
*dst++ = (int32_t) ((uint32_t) ((left > > 1) + (right > > 1)) & 0xffffff00ul);
}
tud_audio_write((uint8_t *)mic_buf, (uint16_t) (spk_data_size / 2));
spk_data_size = 0;
}
}
}
6 功能验证测试
将uac2_headset 音频设备插入PC,在计算机管理->设备管理器->音频输入和输出里面出现耳机和麦克风两个TinyUSB headset设备证明枚举成功。

图5 设备管理器音频设备
电脑端播放音乐使用抓包工具抓到ISOC的数据包:

图6 ISOC数据包