在Linux user space application上使用kernel space密码学算法,详细运作流程可分成下列三个主要步骤:
1. Kernel space (Kernel Space Cryptographic Implementation)
在Kernel space密码学算法实作上,主要分成软件以及硬件运算
- 软件运算(Software calculation) 由CPU进行密码学算法运算,不需额外硬件,但很耗费CPU性能.Linux Kernel原始码位于crypto subsystem底下
- 硬件加速(Hardware component) 由硬件辅助进行密码学算法运算(offloading),不需耗费CPU性能,但需要额外硬件.
SoC Component–许多ARM SoC厂商都会将硬件加解密元件放入SoC中,Linux Kernel原始码多位于drivers/crypto底下.且设计必须遵照Linux crypto framework,不能私下修改。
TPM –专门针对保护密钥与密码运算而设计的一个高安全性的硬件安全芯片,Linux Kernel原始码位于drivers/char/tpm底下。
另外像Intel有推出CPU instructions–Intel® AES NI [9].这或许也算硬件加速的一种.
2. Crypto API–User space interface
主要的功能是提供界面,让user space可存取kernel space.目前主流为cryptodev以及af_alg
- CRYPTODEV [12] 不在Linux Kernel中,需要额外下载,编译并挂载kernel module
- 使用ioctl界面 从OpenBSD Cryptographic Framework移值过来 OpenSSL早期即支持cryptodev
- AF_ALG Linux Kernel 2.6.38开始纳入,原始码位于crypto/af_alg.c
- 使用netlink界面 OpenSSL v1.1.0开始支持AF_ALG (note:除此之外,OpenSSL v1.1.0加入ChaCha20 & Poly1305加解密算法并且移除SSv2)
cryptodev官网上表示使用cryptodev性能较AF_ALG好,但根据[17]的实验,性能其实差异不大.
个人认为新开发的程序可以考虑使用AF_ALG.毕竟AF_ALG在mainline Kernel中–稳定性,兼容性以及维护性都会比较好.
3. User space密码学函式库(Cryptography libraries)[7]
以下为较常见的User space密码学函式库[19],
- OpenSSL
- wolfSSL
- GnuTLS
个人推荐OpenSSL.除了牌子老,使用者众外.OpenSSL也被Linux Foundation下Core Infrastructure Initiative所资助。
OpenSSL提供AF_ALG以及cryptodev的engine,可透过engine来存取Crypto API.但这边要注意的是,Debian中OpenSSL套件预设关闭AF_ALG以及cryptodev选项.所以直接执行会使用user space的密码学算法实作.若想要使用kernel space的密码学算法实作,需下载原始码下来设定并重新编译.
- 开启OpenSSL AF_ALG engine步骤
- 修改debian/rules,在CONFARGS最后面加入enable-afalgeng
- 开启OpenSSL cryptodev engine步骤
- 1.下载cryptodev后,将crypto/cryptodev.h [21]复制一份到OpenSSL/crypto底下
- 2.修改debian/rules,在CONFARGS最前面加入-DHAVE_CRYPTODEV -DUSE_CRYPTDEV_DIGESTS 编译完的OpenSSL即可存取Kernel space密码学算法.
PART ONE--Crypto Subsystem of Linux Kernel
介绍由应用层所发出的crypto(cryptography)request,透过system call将request传送到Linux kernel端,并经由crypto subsystem将request转发给硬件算法引擎(hardware crypto engine)的流程。
概览
Crypto subsystem是Linux系统中负责处理crypto request的子系统,除了包含流程控制机制之外,另一个重要特色就是提供算法实作的抽象层,让各家厂商能够依据需求去客制化实作方式。
其中一个常见例子就是厂商 在硬件构架中加入用以加速特定算法运算效率的硬件算法引擎 ,并且透过crypto subsystem将驱动硬件算法引擎的流程整合进Linux系统中,供其他kernel module或是应用层使用。
一般芯片厂商都会这么玩,至少在我接触的厂商中,因为集成使用openssl软件库去计算的时候会影响整个产品的性能,一般都会使用硬件来替换软件实现,之前我也发的关于硬件IP的就是用来做运算的IP。
以下以openSSL library如何将crypto request传送到kernel crypto subsystem为例子:
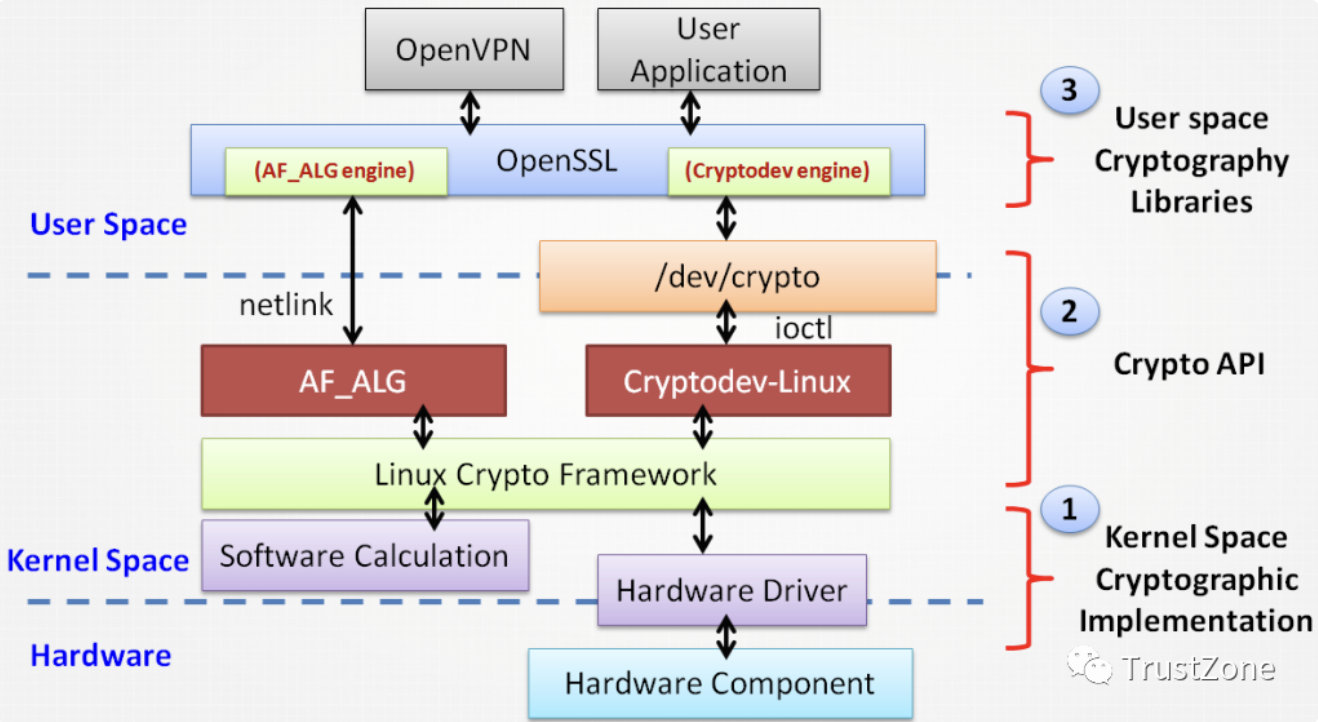
image from: Linux Kernel
cryptodev Engine
在Linux系统中,想要实现应用层与硬件装置的沟通,第一个想到的就是透过character/block device driver,让应用程序开启表示此硬件装置的抽象层,并且藉由读写行为与硬件装置进行互动。
而Cryptodev-linux就是负责此角色,它提供中间层的服务,接收由应用层传送过来的crypto request,再呼叫Linux kernel crypto Subsystem的crypto API将request转发给特定的硬件算法引擎。
Cryptodev-linux为miscellaneous device类型的kernel module,预设路径是/dev/crypto,使用ioctl file operation cryptodev_ioctl来接受应用端所传递过来的数据。
1// https://github.com/cryptodev-linux/cryptodev-linux/blob/master/ioctl.c
2
3static const struct file_operations cryptodev_fops = {
4 .owner = THIS_MODULE,
5 .open = cryptodev_open,
6 .release = cryptodev_release,
7 .unlocked_ioctl = cryptodev_ioctl,
8#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
9 .compat_ioctl = cryptodev_compat_ioctl,
10#endif /* CONFIG_COMPAT */
11 .poll = cryptodev_poll,
12};
13
14static struct miscdevice cryptodev = {
15 .minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,
16 .name = "crypto"
17 .fops = &cryptodev_fops,
18 .mode = S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR|S_IRGRP|S_IWGRP|S_IROTH|S_IWOTH,
19};
20
21static int __init
22cryptodev_register(void)
23{
24 int rc;
25
26 rc = misc_register(&cryptodev);
27 if (unlikely(rc)) {
28 pr_err(PFX "registration of /dev/crypto failedn");
29 return rc;
30 }
31
32 return 0;
33}
应用端则是使用cryptodev.h定义好的struct crypt_op或是struct crypt_auth_op来组成指定crypto request,并呼叫ioctl system call将request送给Cryptodev-linux。
1// https://github.com/cryptodev-linux/cryptodev-linux/blob/master/crypto/cryptodev.h
2
3struct crypt_auth_op {
4 __u32 ses; /* session identifier */
5 __u16 op; /* COP_ENCRYPT or COP_DECRYPT */
6 __u16 flags; /* see COP_FLAG_AEAD_* */
7 __u32 len; /* length of source data */
8 __u32 auth_len; /* length of auth data */
9 __u8 __user *auth_src; /* authenticated-only data */
10
11 /* The current implementation is more efficient if data are
12 * encrypted in-place (src==dst). */
13 __u8 __user *src; /* data to be encrypted and authenticated */
14 __u8 __user *dst; /* pointer to output data. Must have
15 * space for tag. For TLS this should be at least
16 * len + tag_size + block_size for padding */
17
18 __u8 __user *tag; /* where the tag will be copied to. TLS mode
19 * doesn't use that as tag is copied to dst.
20 * SRTP mode copies tag there. */
21 __u32 tag_len; /* the length of the tag. Use zero for digest size or max tag. */
22
23 /* initialization vector for encryption operations */
24 __u8 __user *iv;
25 __u32 iv_len;
26};
Sample code for Cryptodev-linux ioctl:
1// setup data for your crypto request
2 cryp.ses = ctx- >sess.ses;
3 cryp.iv = (void*)iv;
4 cryp.op = COP_DECRYPT;
5 cryp.auth_len = auth_size;
6 cryp.auth_src = (void*)auth;
7 cryp.len = size;
8 cryp.src = (void*)ciphertext;
9 cryp.dst = ciphertext;
10 cryp.flags = COP_FLAG_AEAD_TLS_TYPE;
11
12 // call ioctl to pass a crypto request to `/dev/crypto`
13 if (ioctl(ctx- >cfd, CIOCAUTHCRYPT, &cryp)) {
14 perror("ioctl(CIOCAUTHCRYPT)");
15 return -1;
16 }
另外,Cryptodev-linux也提供session机制,每个crypto request对应到一个session,而session管理当前crypto request的状态。
例如,目前session在initialized的状态,则表示此crypto request可执行encrypt,透过此方式来确保crypto request会在正确的流程下运作。
Linux Kernel Crypto Subsystem
Crypto request会透过kernel crypto API传到kernel crypto subsystem中。以下为简略的crypto API调用流程:
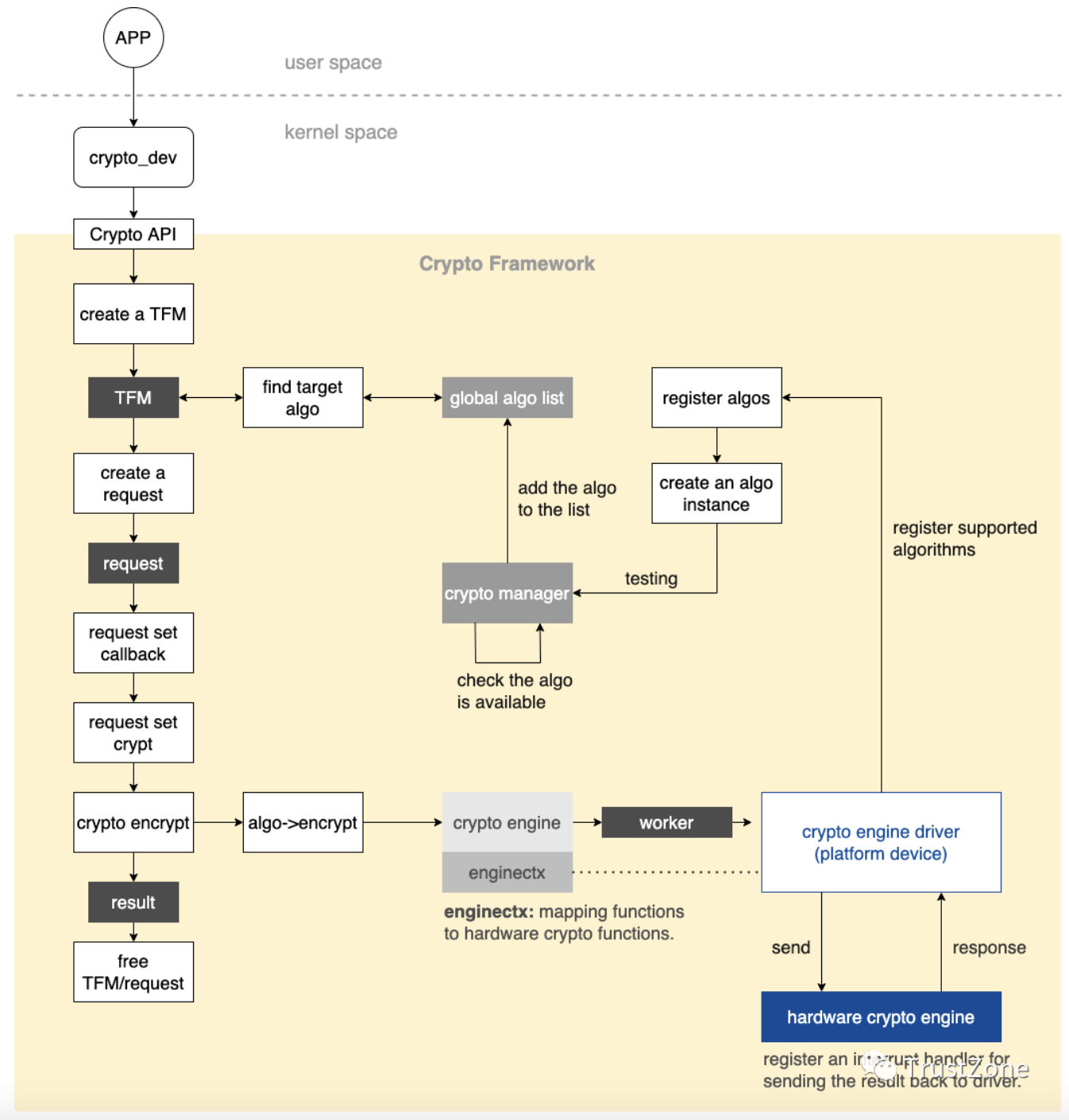
Transformation Object & Transformation Implementation
首先Crypto subsystem有两个重要元素:
- transformation object
- transformation implementation。
transformation object在API中会简写为tfm,又被称作cipher handler;
而transformation implementation则是transformation object底层的实作内容,又被称作crypto algo ,以之前例子来说就是crypto engine的算法实作。
之所以要区分成object和implementation,最主要的原因是有可能多个object会使用同一个implementation。
举例来说,A和B使用者都要使用hmac-sha256算法,因此会新建立A和B两个transformation object并包含A和B各自拥有的key值,但这两个object有可能会使用同一个transformation implementation来呼叫同一个crypto engine进行算法运算。
TFM: The transformation object (TFM) is an instance of a transformation implementation. There can be multiple transformation objects associated with a single transformation implementation. Each of those transformation objects is held by a crypto API consumer or another transformation. https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/crypto/intro.html
1struct crypto_tfm {
2 u32 crt_flags;
3 int node;
4 void (*exit)(struct crypto_tfm *tfm);
5 struct crypto_alg *__crt_alg; // crypto algorithm or transformation implementation
6 void *__crt_ctx[] CRYPTO_MINALIGN_ATTR;
7};
- 当有crypto request进来,会先根据request中指定的算法名称,从已注册的crypto algorithm list中取出适合的crypto algorithm,并新建立transformation object。
- 之后,transformation object会再被组成crypto subsystem所用的cipher request。cipher request有可能共享同一个transformation object,举例来说,hmac-sha256的transformation object包含了transformation implementation和一个key值,而这个transformation object可以使用在多个cipher request的messsage上进行hash算法(不同plaintext使用同一把key进行运算)。
- 当cipher request完成相关设值之后,接着实际调用transformation object的transformation implementation执行算法运算。
此时会出现一个问题,就是当短时间有多个request进来时,我们该如何依序地处理request?
这点crypto subsystem也设计了方便的struct crypto_engine,crypto engine提供了queue管理机制,让多个request能够顺序地转发给对应的crypto engine。
当然如果我们有额外的需求,也可以自己实作其他机制来管理,不一定要使用crypto engine。
1struct crypto_engine {
2 char name[ENGINE_NAME_LEN];
3 bool idling;
4 bool busy;
5 bool running;
6
7 bool retry_support;
8
9 struct list_head list;
10 spinlock_t queue_lock;
11 struct crypto_queue queue;
12 struct device *dev;
13
14 bool rt;
15
16 // implement these three functions to trigger your hardware crypto engine
17 int (*prepare_crypt_hardware)(struct crypto_engine *engine);
18 int (*unprepare_crypt_hardware)(struct crypto_engine *engine);
19 int (*do_batch_requests)(struct crypto_engine *engine);
20
21 struct kthread_worker *kworker;
22 struct kthread_work pump_requests;
23
24 void *priv_data;
25 struct crypto_async_request *cur_req;
26};
Register an Crypto Algorithm (Transformation Implementation)
介绍完crypt API流程后,可以知道要新增transformation implementation到crypto subsystem,最重要的就是注册transformation implementation到crypto algorithm list中。
而Crypto API提供了相关注册API,以stm32-cryp为例:
1struct skcipher_alg {
2 int (*setkey)(struct crypto_skcipher *tfm, const u8 *key,
3 unsigned int keylen);
4 int (*encrypt)(struct skcipher_request *req);
5 int (*decrypt)(struct skcipher_request *req);
6 int (*init)(struct crypto_skcipher *tfm);
7 void (*exit)(struct crypto_skcipher *tfm);
8
9 unsigned int min_keysize;
10 unsigned int max_keysize;
11 unsigned int ivsize;
12 unsigned int chunksize;
13 unsigned int walksize;
14
15 struct crypto_alg base;
16};
17
18static struct skcipher_alg crypto_algs[] = {
19{
20 .base.cra_name = "ecb(aes)"
21 .base.cra_driver_name = "stm32-ecb-aes"
22 .base.cra_priority = 200
23 .base.cra_flags = CRYPTO_ALG_ASYNC,
24 .base.cra_blocksize = AES_BLOCK_SIZE,
25 .base.cra_ctxsize = sizeof(struct stm32_cryp_ctx),
26 .base.cra_alignmask = 0xf
27 .base.cra_module = THIS_MODULE,
28
29 .init = stm32_cryp_init_tfm,
30 .min_keysize = AES_MIN_KEY_SIZE,
31 .max_keysize = AES_MAX_KEY_SIZE,
32 .setkey = stm32_cryp_aes_setkey,
33 .encrypt = stm32_cryp_aes_ecb_encrypt,
34 .decrypt = stm32_cryp_aes_ecb_decrypt,
35},
36}
上述建立含有算法实作的transformation implementation后,接着呼叫注册API:
1ret = crypto_register_skciphers(crypto_algs, ARRAY_SIZE(crypto_algs));
2if (ret) {
3 dev_err(dev, "Could not register algsn");
4 goto err_algs;
5}
即可完成注册。
另外,代码中提及的structure member中, cra_priority代表各transformation implementation的优先程度 ,举例来说,AES-ECB有注册软件和硬件两种不同的transformation implementation,优先程度较高的会先被采用。
cra_priority
Priority of this transformation implementation. In case multiple transformations with same cra_name are available to the Crypto API, the kernel will use the one with highest cra_priority.
PART TWO--Crypto Subsystem of Linux Kernel - Asynchronous & Synchronous
在crypto subsystem中,crypto API分成asynchronous(异步)和synchronous(同步)两种机制。
最早版本的crypto API其实只有synchronous crypto API,但随着要处理的数据量增加,运算和数据传输时间也可能大幅拉长,此时synchronous crypto API有可能让处理流程陷入较长时间的等待,因此后来引入了asynchronous crypto API,供使用者依据自己的使用场景来选择适合的机制。
而asynchronous与synchronous crypto API在命名设计上有所区别,asynchronous会在前缀多加一个a字,反之synchronous则是s字,以hash为例:
1// asynchronous API
2int crypto_ahash_digest(struct ahash_request *req);
3
4// synchronous API
5int crypto_shash_digest(struct shash_desc *desc, const u8 *data,
6 unsigned int len, u8 *out);
除了命名之外,由于两种机制的处理流程不同,因此所需的参数也会有所不同。
以下同样以hash crypto algorithm为例子,说明synchronous和asynchronous crypto API的差异和使用情境。
Synchronous hash API
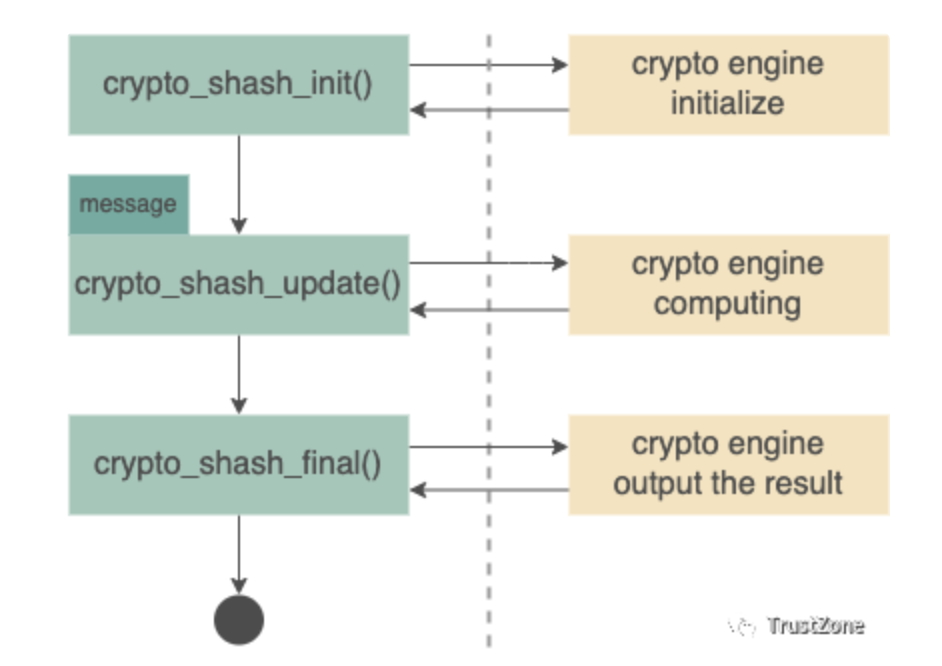
Synchronous hash API中有一个重要的参数struct shash_desc * desc,它是state handler,用以保存运算流程中所需的状态数值。
例如,在API的呼叫流程中,crypto_shash_update()可以被多次呼叫,让使用者可以放入多组需要进行运算的message,而当crypto engine运算完一组message后,可能有些中间状态是需要被保存起来的,这些状态数值就会放在state handler中。
1struct shash_desc {
2 struct crypto_shash *tfm;
3
4 // store required state for crypto engine
5 void *__ctx[] __aligned(ARCH_SLAB_MINALIGN);
6};
因此当使用者在呼叫API前,会需要自己分配一块足够大小的內存,以让crypto engine能够存放这些状态 。在transformation implementation中会设定好crypto engine所需的状态储存空间大小,使用者只需要呼叫特定API即可取得。
1unsigned int size;
2struct crypto_shash *hash; // transformation object or called cipher handler
3struct shash_desc *desc; // state handler
4
5hash = crypto_alloc_shash(name
0
0); // create a transformation object
6
7// get a required desc size for crypto engine via `crypto_shash_descsize` API
8size = sizeof(struct shash_desc) + crypto_shash_descsize(hash);
9desc = kmalloc(size, GFP_KERNEL);
建立好shash_desc之后,接着执行初始化的API,
这个API主要会呼叫transformation implementation的init function,用意是让对应的crypto engine能够进行初始化或是重置等,以准备接下来的运算行为。
1int rc;2rc = crypto_shash_init(desc);3// error handling
初始化完成后,就可以将呼叫update API来对指定的message进行hash运算。
1rc = crypto_shash_update(desc, message, message_len);2// error handling
最後,呼叫 final 來取得 hash 結果。
1 u8 result[DIGEST_SIZE];2 rc = crypto_shash_final(desc, result);3 // error handling
基本上synchronous API使用方式跟一般应用端的crypto library很相似,只要顺序的呼叫对应流程的API,并且针对返回的结果进行error handling即可。
Synchronous crypto API用起来虽然直观,但是却不适用于一些场景,除了一开始有提到synchronous机制会造成block之外,另一个可能的问题是,当需要处理的数据为不连续內存区段时,synchronous crypto API就不是这么好用。
可以看到之前所提及的例子,其中crypto_shash_update的输入参数message为一段连续內存的buffer,假设目前有好几段数据,那就必须要呼叫crypto_shash_update多次,才能够传入所有的数据。
Asynchronous hash API